Java hello world program....using servlet
Before that ask yourself, What is servlet?
WHAT IS SERVLET for this question I have many answers .
Servlet is Application Programming Interface what we called API (kind of interfaces )
Or
Servlet is a technology
oR
Servlet is a Programming language used to create web application
OR
Servlet is a Class it works like a server (Giving response to the incoming request)
oK today we learn hello world program in java servlet later we learn something in-depth.
Before going to see hello world in servlet just navigate java hello world in eclipse that would easy to know the difference between java and java servlet
Step 1:
Open your eclipse click file -> New -> and select Project
(don't scold me .... I know you know thizzzz.....)
Step 2:-
Now You can see the above window Click web -> Dynamic web Project
(finally .... :-) )
Step 3:-
Give your project name....if you don't like your project name just give mine
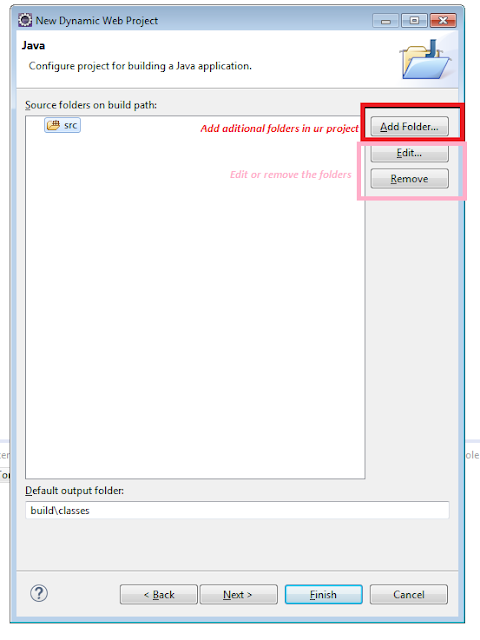
Step 4:-
You can create, Edit, and Remove the folder in the above window...
(just try it yaar....)
Step 5:-
Now you can see your Context root and directory... just check the below check box.
(This will automatically create web.xml in the project)
Step 6:-
Now you can see your project in your project explorer....
Step 7:-
In your application navigate to the src folder and right click
Click New->Class
Step 8:-
Source folder name is the name of your folder which contain all the source
package (what is package?) name you can create more package (folders) by using dot (.)
Step 9:-
Step 10:-
You can see your program in notepad
Step 11:-

You can copy from here....
package com.servletHelloWorld.hello;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
Yup, now what is import ? and why we use import?
import is a keyword, class libraries can be imported by using import keyword
example :-
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse
or
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
Both are same ... * will take everything form the library otherwise just mention the libraries like above.
Step 12:-
what is ....?
public class Hello extends HttpServlet {
}
I think you know public (if ur not click and read)
Hello is the class name ... in Step 8 you gave Hello in the Name field and modifiers public.
what is extends ?
Extends is a keyword used for extending .... we create a class Hello (consider this is a Sub class) and we extends HttpServlet (this is super class)
we are extending the sub class form the super class ,it maybe difficult to understand don't worry we ill discuss this with IMPLEMENTS..
ok now what? let's see inside the class
public void init()
{
}
This is the method called init() called only once ...this is for one time initialization
this method called when the first time of servlet created.
public void doPost()
{
}
doPost has no limitations on parameter ,faster and secured
public void doGet()
{
}
doGet only limited data ,request shown in address bar.
public void destroy()
{
}
we destroy the objects using this destroy method
Step 13:
This is the coding you can copy the coading from here..
package com.servletHelloWorld.hello;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class Hello extends HttpServlet {
public void init() throws ServletException
{
super.init();
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException
{
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter output = res.getWriter();
output.println("<h1>Hellooo</h1>");
output.println("<h2>Helloo</h2>");
output.println("<h3>Hello</h3>");
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException
{
}
public void destroy()
{
super.destroy();
}
}
Step 14 :
Yep here we are ... don't ask where...
GO BACK TO STEP 5 and read inside the red box...
yes that will generate the web.xml file now we have to open the xml fileeee.....and copy paste the below coding or do type manually (copy and paste I won't tell to any one)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>servletHelloWorld</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Sample</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.servletHelloWorld.hello.Hello</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Sample</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Okay ... <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> this is xml version
you have to create xml name space and schema location with id and version...
<display-name>servletHelloWorld</display-name>
display the name of ur project
<servlet> </servlet>
this is the method to create servlet name and class ..inside this <servlet> tag write servlet name and class
<servlet-class>com.servletHelloWorld.hello.Hello</servlet-class>
goto step 8 and u can fine the class name ...u have give the proper package name with class name.
Mapping
<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Sample</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
servlet mapping name and servlet name should same....
url pattern is the pattern to display the page
Step 15:
start the server
Step 16
Click finish
Step 18:
yeahhh you run the java servlet program....
















Nice way of illustration ..keep up the good work
ReplyDeleteThank you Vignesh C.
Delete